As cybersecurity threats rapidly evolve this digital age is one in which breaches and vulnerabilities have become a common modern reality — from individuals to governments. With more and more cybercriminals becoming smarter by the day, we need security specialists who can keep digital infrastructure safe. This is where ethical hacking come into the picture, an essential tool in the fight against unethical cyber threats to discover and fix a security hole before any mal-practice is done. However, what is ethical hacking and how does it play an important role?
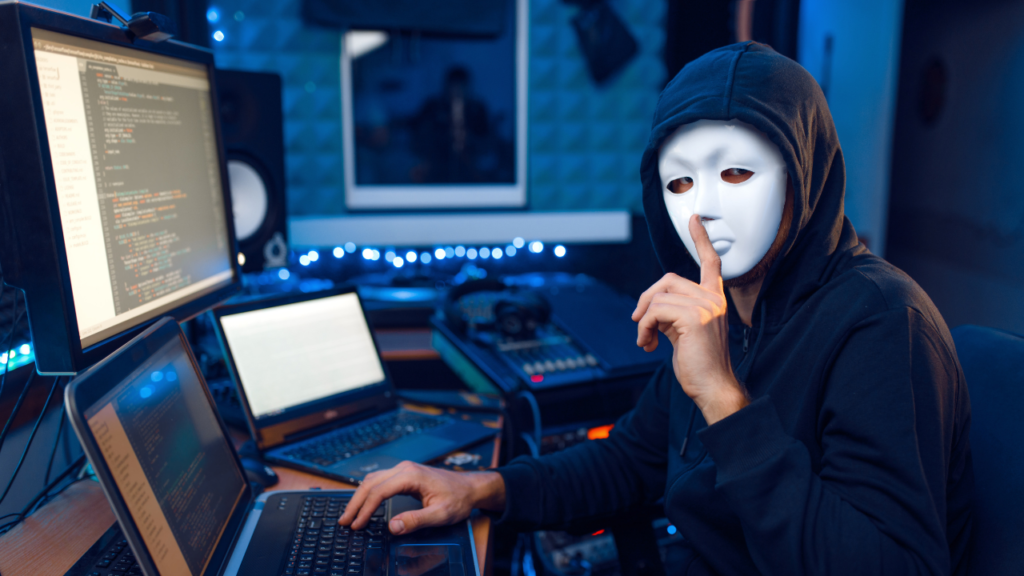

What is Ethical Hacking?
Ethical hacking the term itself defines that you are legally authorised to exploit a computer system/network or applications in an org. But unlike black hat hackers, ethical hackers (or “white hats”) use these skills for good, with permission and within the law. The purpose is to help fortify security by uncovering risks before they can be abused by criminal or black hat hackers.
The tool, method, or techniques used by the cyber criminals are a means to break into our systems and the same tools, methods, or techniques are often used by other hackers known as ethical hackers but with the legal permission of the system owner. They play a critical role in securing systems and protecting against the increasing number of cyberattacks that target personal data, financial information and business operations.
Why Ethical Hacking Matters
Securing Sensitive Data
The information in this world is becoming increasingly digitized, and the significant parts of our lives such as financial data or health record are processed via internet. This is the kind of info that ethical hackers attempt to secure by finding weaknesses in apps and systems which hold or process any such data. Their work helps ensure that people trust the digital systems they rely on.
Preventing Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks are Expensive When these breaches happen, organizations can suffer financial loss, irreparable damage to their reputation and legal liabilities. This is where ethical hacking comes in — to identify and plug these security gaps before they can be used to launch a cyber attack. Businesses need hackers to stay one step ahead of the bad ones
Aligning with Security Principles
All sorts of industries, particularly finance, healthcare and government face tight security regulations to protect sensitive data. Ethical hackers conduct security assessments to ensure that systems meet the required standard by helping organizations comply with these regulations. It is even more important when it comes to escaping fines and penalties involving data breaches.
Building Trust Through Digital Systems
As transactions and services increasingly shift to the cloud, users want confidence that their information is secure. In building this trust ethical hackers work to stay a step ahead by making sure digital platforms are locked down. And that goes double for industries like online banking, e-commerce, and cloud services where a successful breach can be incredibly costly to both consumers and businesses.
HOW TO REACT – NEW/UPSTART Menace
As the cyber threat landscape is always changing, there are new vulnerabilities uncovered virtually every day. It is to these emerging threats that ethical hackers are the first line of defence. Ethical hackers keep a strong awareness about the recent hacking tactics and consequently are able to modify themselves immediately in such a way that it serves as a shield against various risk factors which are present in the cyber arena.
Training and Education
Educational ethical hacking which reads a security guideline playing an important role of the next. They include making users aware of the relevance of powerful passwords, maintaining secure network behavior and how to identify phishing attacks. Their knowledge helps build a stronger security mindset, organizationally and in the world.
The Ethical Hackers Toolkits
Tools & Techniques for an Ethical HackermaniverseMedium
Penetration Testing: Simulating attacks on the systems as would happen in real world.
Vulnerability Scanning — The automated network and system vulnerability tools which are used to identify the standard, un-patched or outdated vulnerabilities.
Humans — Social Engineering: An employee pretends to be a company representative in order to obtain confidential information about the enterprise as part of security testing.
Reverse Engineering: study of software, often in search of vulnerable aspects or malicious functionality.
Network Security AuditsAn in-depth assessment of the security of an organization’s network infrastructure including firewalls, routers and switches
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The important thing to remember in all of this as well is ethical hacking must always be legal and within the bounds of the law, and licensed through your organization. To achieve this, ethical hackers strictly follow a code of conduct to prevent their work from causing any harm or encroaching on the privacy of the target. And this is why many ethical hackers work in tandem with security teams, companies, and government agencies to ensure their actions are not only legal but helpful as well.
Conclusion
The modern cybersecurity consists of ethical hacking, which is the need of this hour. Ethical hackers find and fix flaws before bad actors have the chance to exploit them, securing our data, saving us from costly breaches, and helping build faith in the digital systems we depend on. The role of ethical hackers will only be more crucial as the threats that need to be defended against evolve.


0 Comments